Yesterday, the FDA opened for public comment its long-awaited guidance for industry about reducing salt in processed food products. The guidance affects about 150 products. It gives baseline data for those products and sets targets for salt reduction.
Please note that I am using the word salt, not sodium. The targets are for sodium reduction. Most dietary sodium comes from salt added to processed foods and pre-prepared foods. Salt is 40% sodium. The target dietary intake of 2300 mg sodium comes to just under 6 grams of salt a day, which is not particularly low. It is, however, lower than current intake levels.
In a blog post, FDA official Susan Mayne said the link between sodium intake and blood pressure is “strong and well documented,” but
In fact, it’s very difficult in the current marketplace NOT to consume too much sodium. The average intake today is over 3,400 milligrams—significantly more than the 2,300 milligram limit recommended by federal guidelines. And it’s not just adults who are eating too much sodium: Children and teens consume more than is recommended.
Vox, for example, provides a terrific chart on the amounts of sodium in foods. It starts with this:
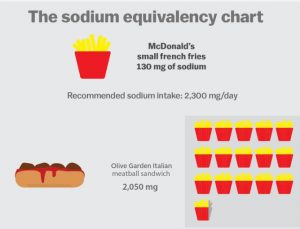
Susan Mayne goes on to explain that
the FDA assessed the sodium content of thousands of products in the marketplace and engaged with experts in industry, academia, and government to get the best available scientific and technical input. We know that sodium has important functions in many foods, such as taste, texture, and microbial safety… Our approach encourages gradually reducing sodium in the majority of foods that contain it…Moreover, our draft targets apply to processed and prepared foods that are eaten both at home and outside the home.
Despite the voluntary nature of the guidance and the lengthy timeline (up to ten years) for implementation, the makers of processed foods are sure to object. At their urging, the House committee on appropriations, in draft report language, urged the FDA to postpone guidance on salt until the CDC and Institute of Medicine update the Dietary Reference Intake standards for sodium intake.
The Salt Institute, the trade association for the salt industry, issued a press release charging malpractice:
The issuance today of new “voluntary” sodium reduction mandates by the FDA is tantamount to malpractice and inexcusable in the face of years of scientific evidence showing that population-wide sodium reduction strategies are unnecessary and could be harmful. This effort will limit the food choices of Americans, not increase them as the FDA claims. It will make our food less safe and endanger public health.
In JAMA, CDC Director Thomas Frieden rebuts the scientific arguments point by point and, in my view, demolishes them. He explains how important this initiative is to public health:
Thirty-nine countries have established sodium targets for foods and meals, with 36 of those adopting voluntary approaches. Setting targets helps create a level playing field for the food industry, supporting reductions already begun by companies such as Walmart, Darden, Unilever, PespsiCo, General Mills, Mars, Nestlé, and others. The United Kingdom set voluntary sodium reduction targets in 2003; from 2003 to 2011 sodium intake decreased 15%. During this same period, average blood pressure decreased, and, following no change in prior years, deaths from ischemic heart disease and stroke decreased by approximately 40% [the reference for this last statement is BMJ Open. 2014;4(4):e004549].
Most people would be healthier cutting down on salt intake. Food company executives know this. Politico Morning Agriculture points out that some Big Food companies have joined the public health community in supporting the FDA’s proposal.
The band of strange bedfellows – the American Heart Association, Mars, Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, Nestlé, PepsiCo, American Public Health Association, Unilever and the Center for Science in the Public Interest – all signed on to a letter last month to Senate Appropriations ag subcommittee Chairman Jerry Moran and ranking member Jeff Merkley to support the FDA on sodium. Find that here.
From a public health perspective, the FDA initiative is a step in the right direction but could go further. It should have required mandatory salt reduction. Judging from the Salt Institute’s reaction, this is still a big step. The New York Times quotes Michael Jacobson:
“The F.D.A. found a sweet spot between doing nothing and regulating…This will at least give the public benchmarks against which we can gauge sodium content of foods.”
FDA resources:




