GAO tells USDA to get busy on worker safety at meat-packing plants
The summer is a good time to catch up on reports. Early in July, the US Government Accountability Office (GAO)—a government watchdog agency—sent a firm letter to USDA chiding that agency for not implementing GAO’s recommendations in a timely manner.
In November 2020, we reported that on a government-wide basis, 77 percent of our recommendations made 4 years ago were implemented…[but] USDA’s recommendation implementation rate was 46 percent. As of May 2021, USDA had 171 open recommendations. Fully implementing all open recommendations could significantly improve USDA’s operations.
Among the GAO’s recommendations were two of particular interest:
I. Strengthen Protections for Wage Earners. See: Workplace Safety and Health: Better Outreach, Collaboration and Information Needed to Help Protect Workers at Meat and Poultry Plants. GAO-18-12. Washington, D.C.: November 9, 2017.
Recommendation: The FSIS Administrator should work with the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) to assess the implementation of their agencies’ joint memorandum of understanding (MOU) regarding worker safety at meat and poultry plants and make any needed changes to ensure improved collaboration, and also set specific time frames for periodic evaluations of the MOU.
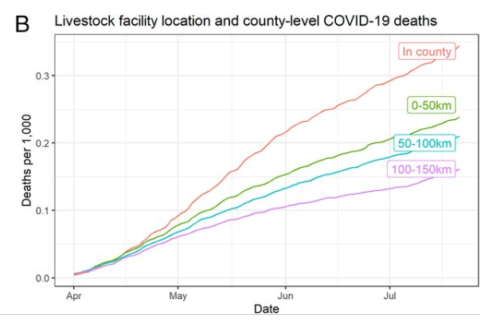
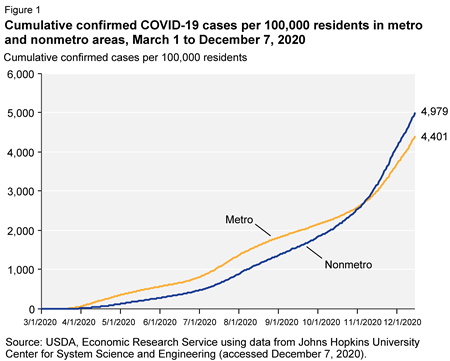
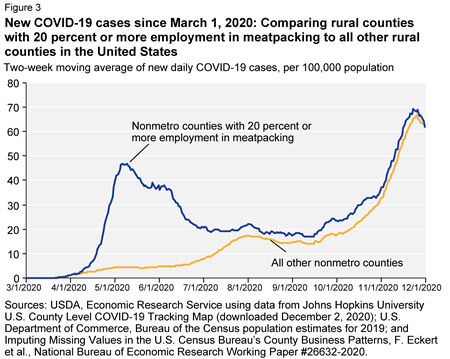
Comment: This is about the failure of OSHA and USDA to protect meat-processing and -packing workers from Covid-19 (for data on the effects of Covid-19 on these workers, see Leah Douglas’s regular reports on the Food and Environment Reporting Network. GAO is essentially calling on the two agencies to get busy on protecting workers at those plants.
II. Improve Cybersecurity. See Cybersecurity: Agencies Need to Fully Establish Risk Management Programs and Address Challenges. GAO-19-384. Washington, D.C.: July 25, 2019.
Recommendations: The USDA should (1) develop a cybersecurity risk management strategy that includes the key elements identified in this report; and (2) establish and document a process for coordination between cybersecurity risk management and enterprise risk management functions.
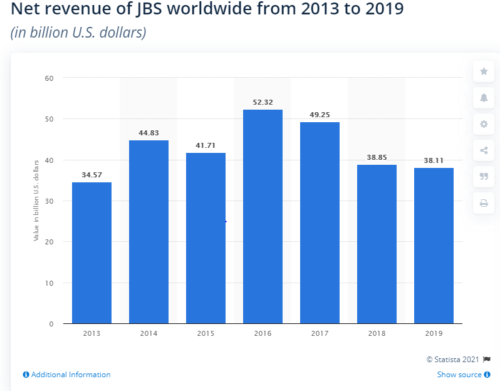
Comment: The GAO is asking USDA to work with other agencies to improve cybersecurity at meat-processing plants. Why? Because the meat industry’s weak cybersecurity—a long-standing problem—was recently exposed when hackers did a ransomware attack on JBS meat plants that cost the company $11 million to resolve.